FTA History / Legacy

FTA Origins
Paul Paris and Del Research Corporation
FTA has a legacy that is tied to the birth of modern fracture mechanics. The great Paul C. Paris, who received his PhD in applied mechanics from Lehigh University in 1962 (a year after publishing his paper defining the now famous empirical Paris Law that bears his name), and who was ultimately awarded the distinguished Wöhler Medal by the European Structural Integrity Society (ESIS) in 2016 for his seminal contributions to fatigue crack propagation, became a Full Professor at Lehigh University in 1965. It was at this time that Paul established a prodigious fracture mechanics research group at Lehigh University that included Fazil Erdogan, George Sih, and later, George Irwin and Bob Wei.
Over the next decade, Paul and his team did extensive work on fatigue crack growth in the near-threshold, linear, and high ΔK regimes. Following Elber's discovery of crack closure in 1967, Paul and his research group performed systematic experiments to study the effect of stress ratio and crack closure on fatigue crack growth. It was at this time in 1967 that Paul founded Del Research Corporation in Hellertown, PA, along with George Irwin and Richard Hertzberg, Paul's first graduate student. The company soon became well known with a strong reputation for consulting work in areas of failure analysis and mechanical testing. This success was not surprising given that Del Research hired intrepid young engineers, including Hiroshi Tada and Keith Donald, another Lehigh graduate, and that its list of directors included George Irwin, the father of modern fracture mechanics, and Richard Hertzberg. This strong research team in fracture mechanics, under Paul's leadership, soon established the first Annual Symposium on Fracture Mechanics which was held at Lehigh University in the lecture hall of Whitaker Lab in the late 1960s.


Automated Testing Systems
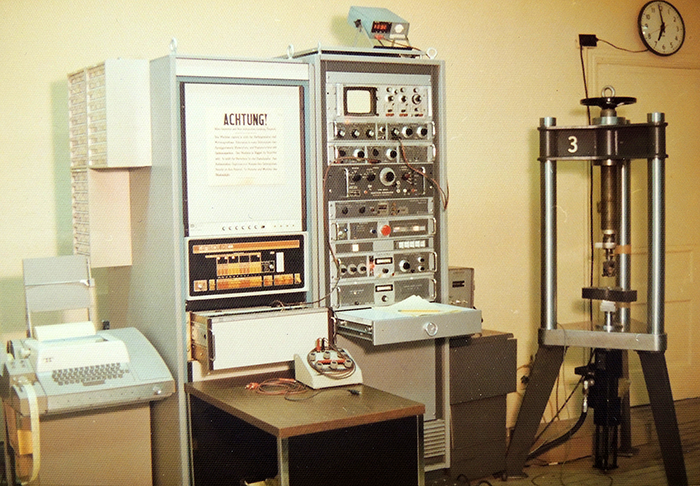
Having performed fatigue crack propagation tests with tedious manual systems for a few years, Del Research pioneered the first automated system for fatigue crack growth testing on a Digital Equipment Corporation PDP-8/e minicomputer in 1972, which revolutionized fatigue crack growth testing. This novel automation meant that manual load shedding and visual observation of crack size were no longer the norm. This automation greatly reduced the scatter in fatigue crack growth test data, which was empirically demonstrated by an ASTM round-robin in the late 1970s. By means of this automation, relatively large load drops of 10% and minimum Δa increments of 0.020 inches for load shedding, which had been the norm for manual load shedding, were no longer required. This automation fostered a generation of testing that would be less tedious and more productive.
This first-generation system was based on assembly language. All code, variables, and utilities were crammed into 4 kB of total memory! Hardware interrupts were essential to real-time data acquisition and control.
J. Keith Donald
With its growing reputation for failure analysis and fatigue testing, J. Keith Donald was hired by Dr. Paul C. Paris at Del Research Corporation in 1972, having received his BS degree in Mechanical Engineering from Lehigh University. A primary role for Mr. Donald included developing software for automated fatigue crack growth testing, on both the first-generation system and subsequent systems that he would later pioneer.
In 1974, he joined ASTM Committee E-24 and contributed to developments in non-linear fracture toughness and sub-critical crack growth. Mr. Donald maintained an active role in promoting the laboratory division of Del Research throughout its existence.
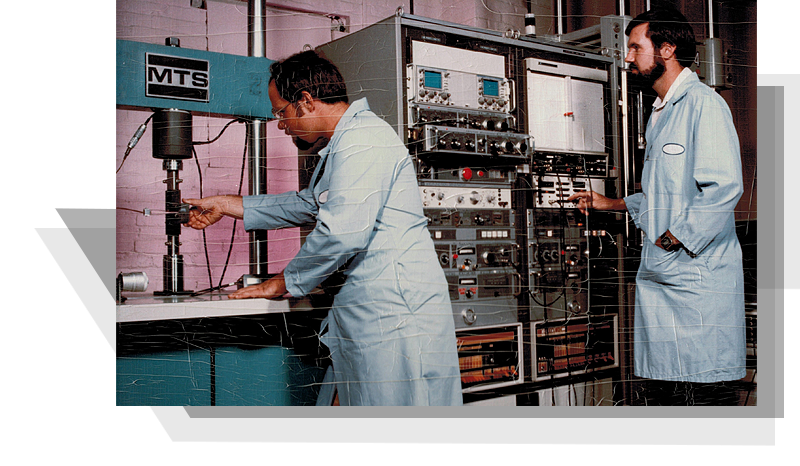
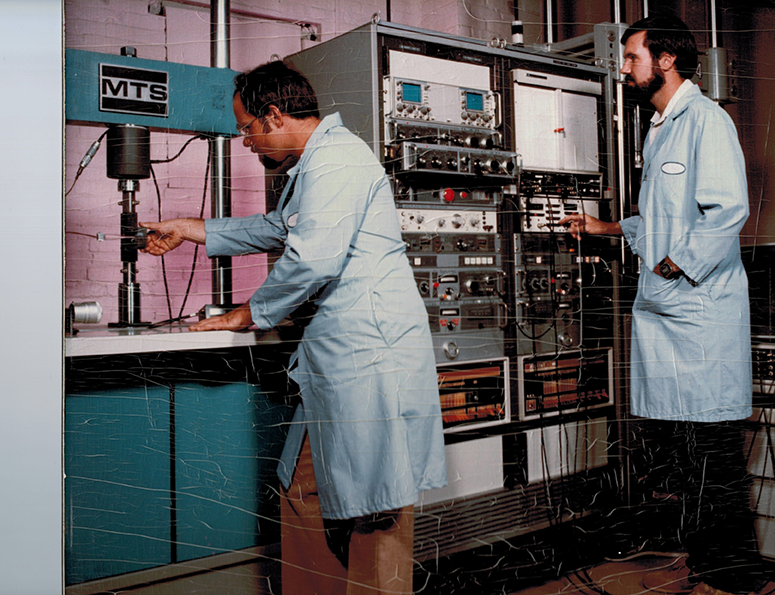




Fracture Technology Associates
In 1984, Mr. Donald formed Fracture Technology Associates (FTA) to further provide software and testing services for fatigue crack growth and fracture toughness testing. In 1985, Mr. Donald developed a second-generation automated fatigue crack growth test system that was built on an IBM PC platform in IBM BASIC, and the first commercial system was sold and installed at Florida Atlantic University. As a pioneer in automated test systems for fatigue and fracture testing throughout his career, Mr. Donald released a third-generation system on the ADwin-Gold DSP platform in 2001. This represented a breakthrough as assembly language was no longer required, with processes occurring independent of the PC and event timers replacing hardware interrupts.
These FTA test systems have since become the de facto gold standard in automated fatigue and fracture testing and were later purchased and used by the likes of NASA, Pratt & Whitney, GE Aviation, GE Energy, Boeing, Lockheed Martin, Honeywell Aerospace, Knolls Atomic Power Laboratory (KAPL), and many others, for critical materials characterization.
Keith Donald Legacy
Mr. Donald is an internationally recognized fracture mechanics expert and was a pioneer in automated fracture mechanics testing and research until his retirement in 2017. He has authored numerous papers on the subject. One of his greatest contributions is the development of the Adjusted Compliance Ratio (ACR) method, which is an available option in the FTA fatigue crack growth software. ACR is a powerful experimental methodology for mitigating the effects of remote closure on crack growth rate measurements that relies on the compliance method for estimating ∆Keff. The ACR method gained mainstream acceptance by the technical community with its inclusion in ASTM E747-15e Appendix X4. Keith was awarded the ASTM E08 Fatigue Lecturer Award in 1997 and the ASTM E08 Award of Merit in 2005. Keith was also awarded the ASTM E08 Coffin-Manson Fatigue Achievement Award in 2009, an award presented to those individuals who have made an outstanding contribution to the field of fatigue testing.


